
Glycaemic index (GI) bands and assignment of polyols, fruits, sugars,... Download Table
FODMAP stands for fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols, which are short-chain carbohydrates (sugars) that the small intestine absorbs poorly. Some people experience digestive distress after eating them. Symptoms include: Cramping Diarrhea Constipation Stomach bloating Gas and flatulence

Pin on Healthy topics
Nectarines Green beans (more than 25 beans contain a moderate amount of sorbitol) Bell peppers (more than 2.8 ounces contains a high amount of sorbitol) Butternut squash (1/2 cup or more contains moderate to high amounts of mannitol)
Pick The Polyols A Label Reading Guide For Beginners FODMAP Friendly
Vegetables with high numbers of polyphenols include: artichokes, with 260 mg polyphenols. chicory, with 166-235 mg polyphenols. red onions, with 168 mg polyphenols. spinach, with 119 mg.

8 foods high in polyphenols and why you should add them to your diet Artofit
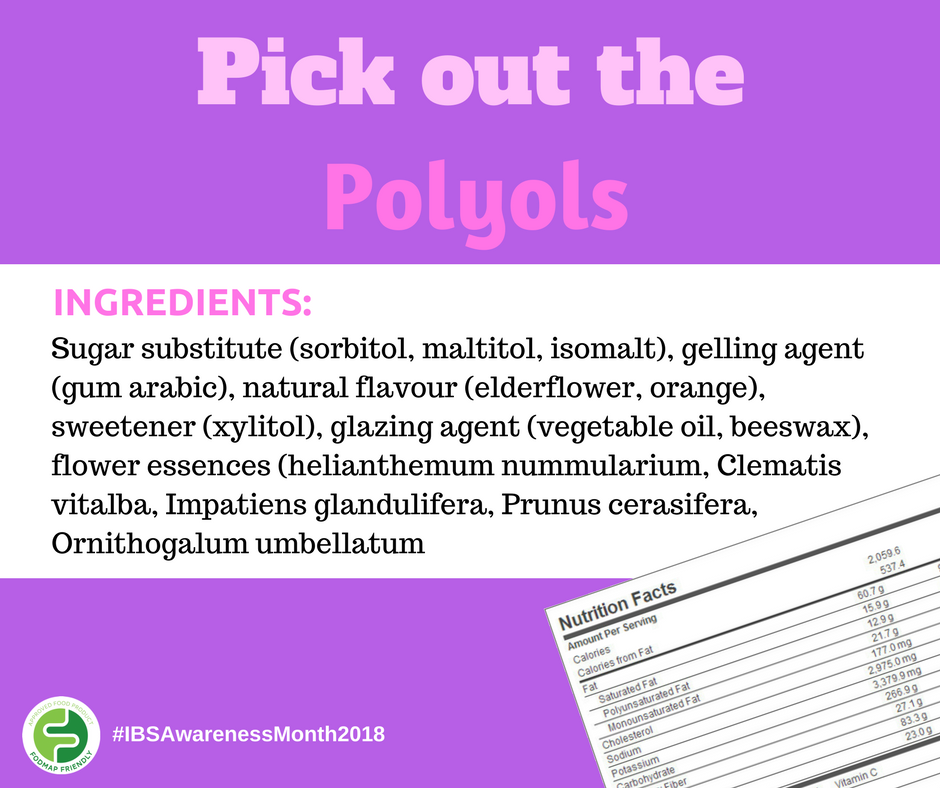
Polyols are present in foods (for example apricots, mushrooms, cauliflower) and also commonly used as artificial sweeteners in sugar free chewing gum, lollies and mints. It is often identifiable by additive numbers on food packaging: Sorbitol (420), Mannitol (421), Maltitol (965), Xylitol (967) and Isomalt (953), along with the mandatory declaration "excessive consumption may have a laxative.

What is a FODMAP Diet? FODMAP diet stands for Fermentable, Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides
Polyphenols are a category of compounds naturally found in plant foods, such as fruits, vegetables, herbs, spices, tea, dark chocolate, and wine. They can act as antioxidants, meaning they can.

Foods High in Polyphenols Polyphenol food list Polyphenols, Polyphenols food, Food
High-FODMAP foods like dairy and legumes cause higher levels of gas and liquid in the intestines. Low-FODMAP fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, seeds, and protein are less likely to cause symtoms like gas and bloating and may be ideal if you are struggling with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). To get the most out of a low-FODMAP diet, work with a.

Polyols A blog by Monash FODMAP The experts in IBS Monash Fodmap
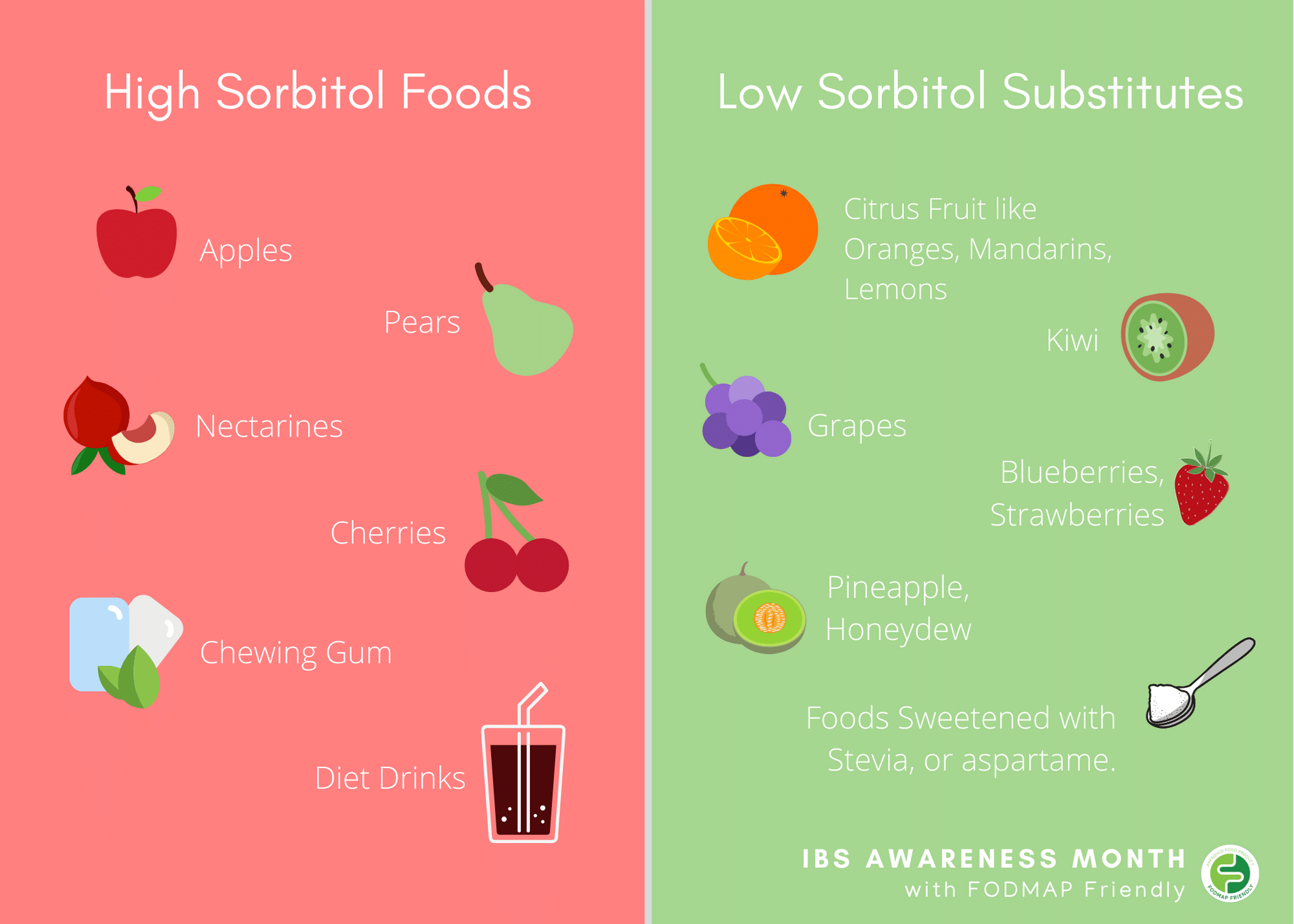
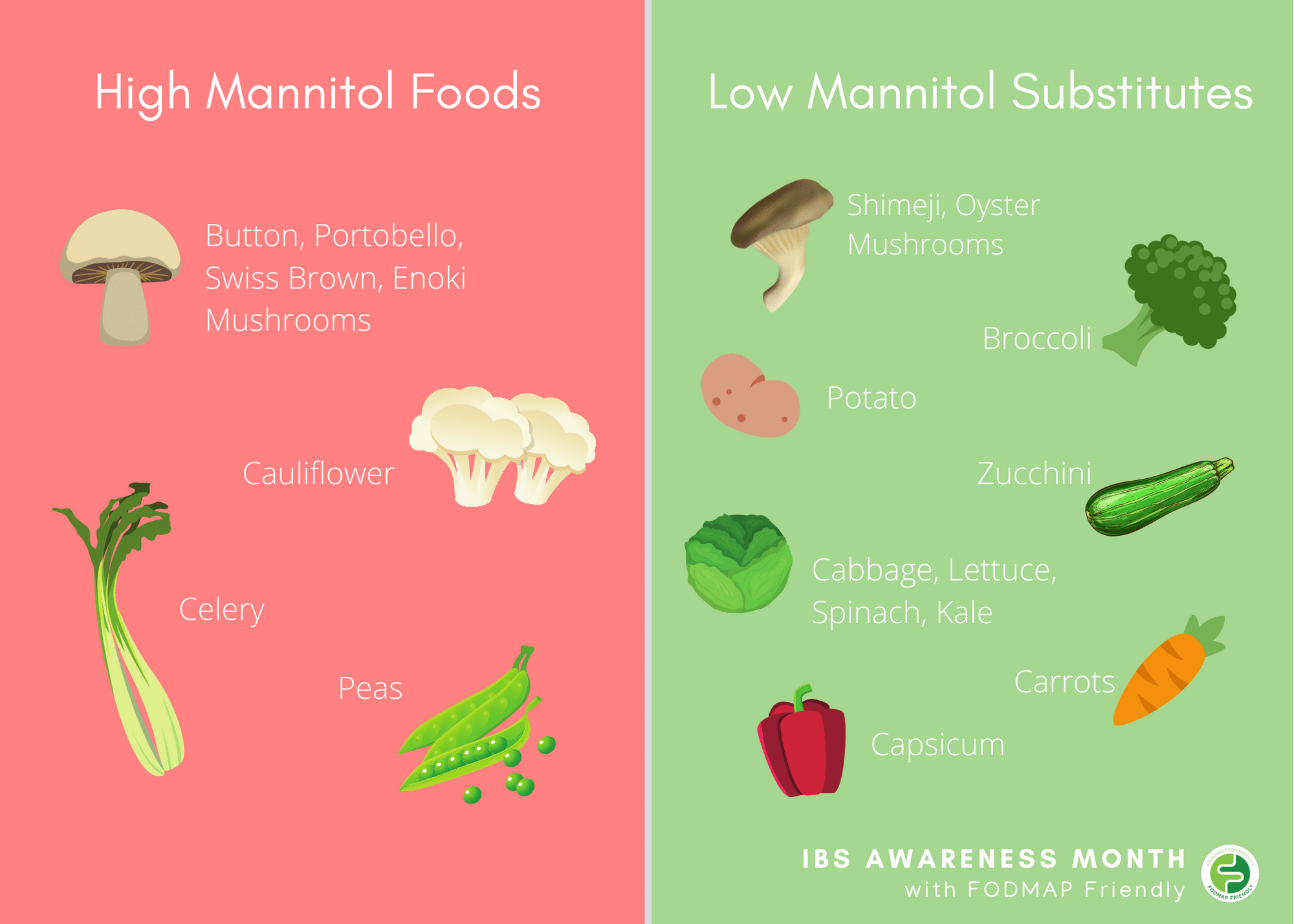
Typical polyols include erythritol, xylitol, sorbitol, and mannitol. They can be produced synthetically, such as erythritol derived from fermented glucose, or xylitol from birch, hardwood trees and fibrous vegetation. Polyols are used commercially as a sweetener.

What Are Polyols? Learn All About the "P" in FODMAP! FODMAP Everyday
The Chemistry of the "P" in FODMAP Polyols are small-chain carbohydrates that occur naturally in certain fruits and vegetables or as additives in packaged foods.

What are Polyols? A Little Bit Yummy
Includes garlic salt, garlic powder. Onions - avoid entirely if possible. Includes onion powder, small pickled onions. FODZYME helps break down the specific FODMAPs found in garlic and onions. Artichoke. Asparagus. Baked beans. Beetroot, fresh. Black eyed peas.
Humans don't absorb polyols so should we avoid them? FODMAP Friendly
In conclusion, while high polyol foods offer numerous health benefits, it is important to be mindful of your own tolerance and any potential side effects. Incorporating a variety of fruits and vegetables into your diet, including those high in polyols, can contribute to a well-rounded and nutritious eating plan. List of High Polyol Foods

The 'O' in FODMAP Oligosaccharides Erin Dishes Nutrition Personalized Elimination Diet Meal
A low FODMAP diet may help reduce symptoms, which will limit foods high in fructose, lactose, Fructans, Galactans, and Polyols. The low FODMAP diet is often used in those with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). The diet could be possibly used in those with similar symptoms arising from other digestive disorders such as inflammatory bowel disease.
Humans don't absorb polyols so should we avoid them? FODMAP Friendly
High FODMAP meaning FODMAP stands for fermentable oligo-, di-, mono-saccharides, and polyols. These are the scientific names for carbs that may cause digestive issues. A food is categorized as.

The 'P' in FODMAP Polyols Erin Dishes Nutrition
Polyols, such as sorbitol, mannitol, xylitol, maltitol and isomalt, mimic the sweetness of sucrose (table sugar), however, because their absorption is much slower, only a small amount of what is eaten is actually absorbed. Polyols are often used as low-calorie sweeteners in sugar-free and diet products.

Polyols A blog by Monash FODMAP The experts in IBS Monash Fodmap
FODMAPs are found in a wide variety of foods, including fruit and vegetables, grains and cereals, nuts, legumes, lentils, dairy foods and manufactured foods. This makes following the FODMAP diet a little tricky, as you cannot simply guess which foods will be high or low in FODMAPs.

40 Foods High in Polyphenols Antioxidants With Net Carbs Kohlenhydratarme lebensmittel
Polyols occur naturally in foods (like fruit and vegetables) or are manmade and added to processed foods as a low calorie sweetener. This is why you often see them in weight loss protein bars and diabetic sweets. Unfortunately sugar alcohols like to wreck havoc on our digestive systems and can cause down right unpleasant irritable bowel.

Polyphenols Health Benefits For Heart & Gut Health Fullscript
Polyols: Polyols, or sugar alcohols, are a type of carbohydrate that humans can only partially digest and absorb in the small intestine. Polyols, such as sorbitol, mannitol, xylitol, maltitol, and isomalt, mimic the sweetness of sucrose. However, because their absorption is much slower, only a small amount of what is eaten is actually absorbed.